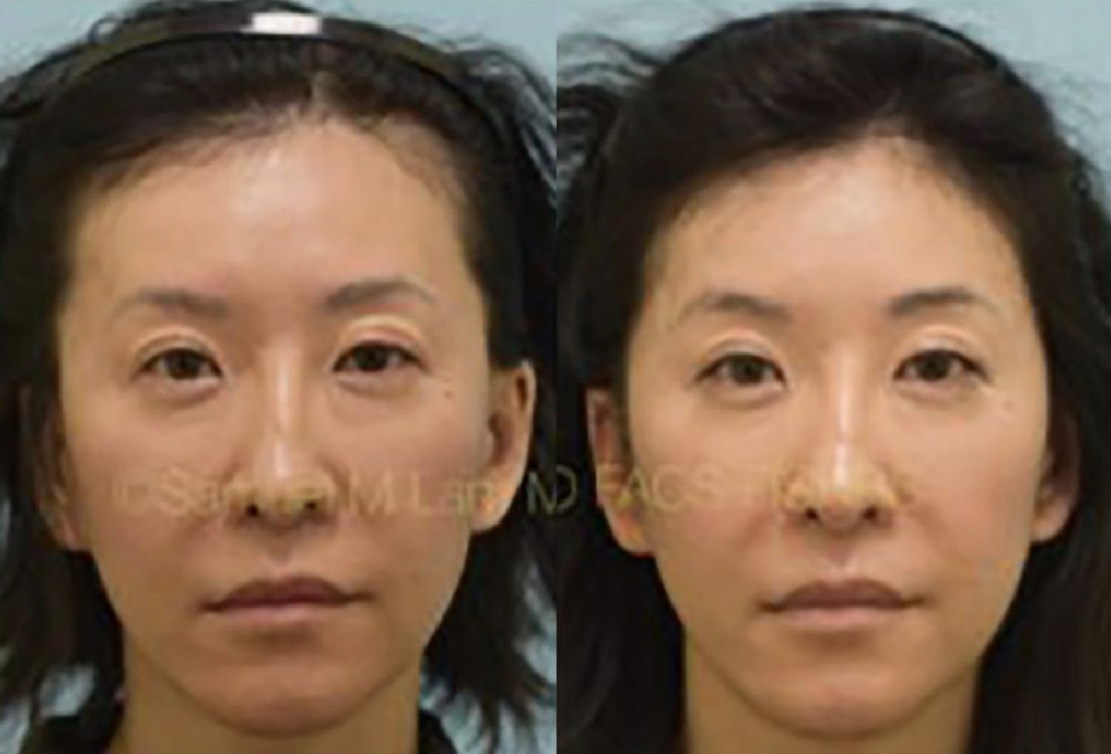
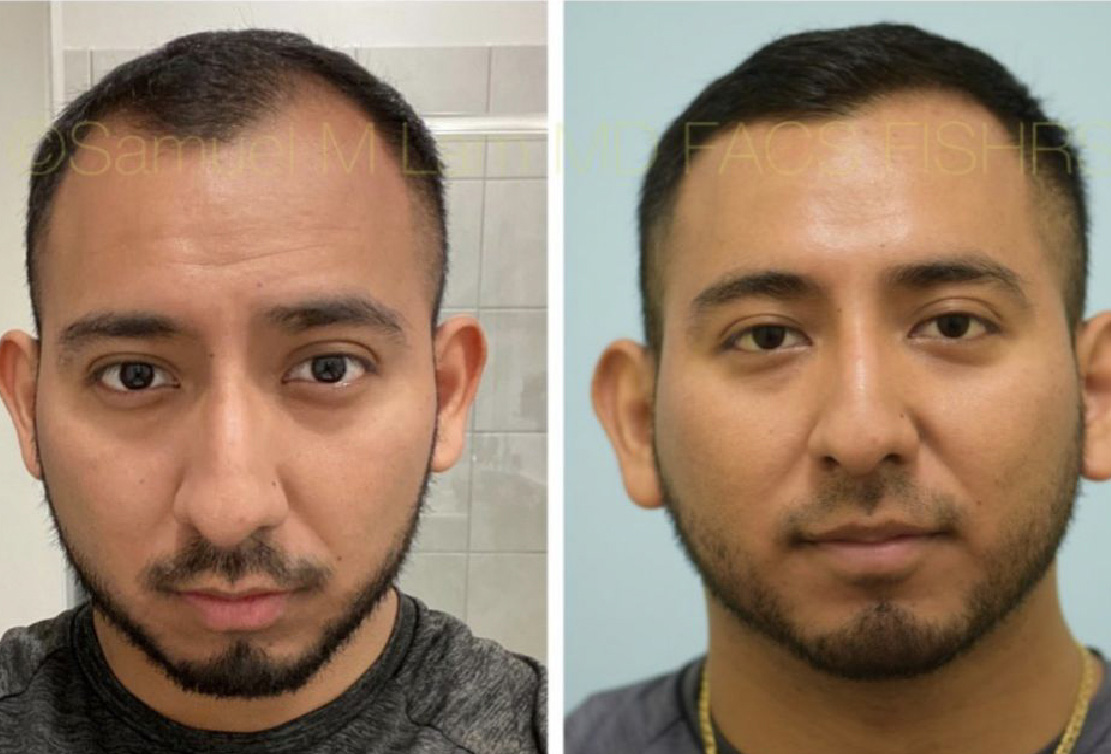
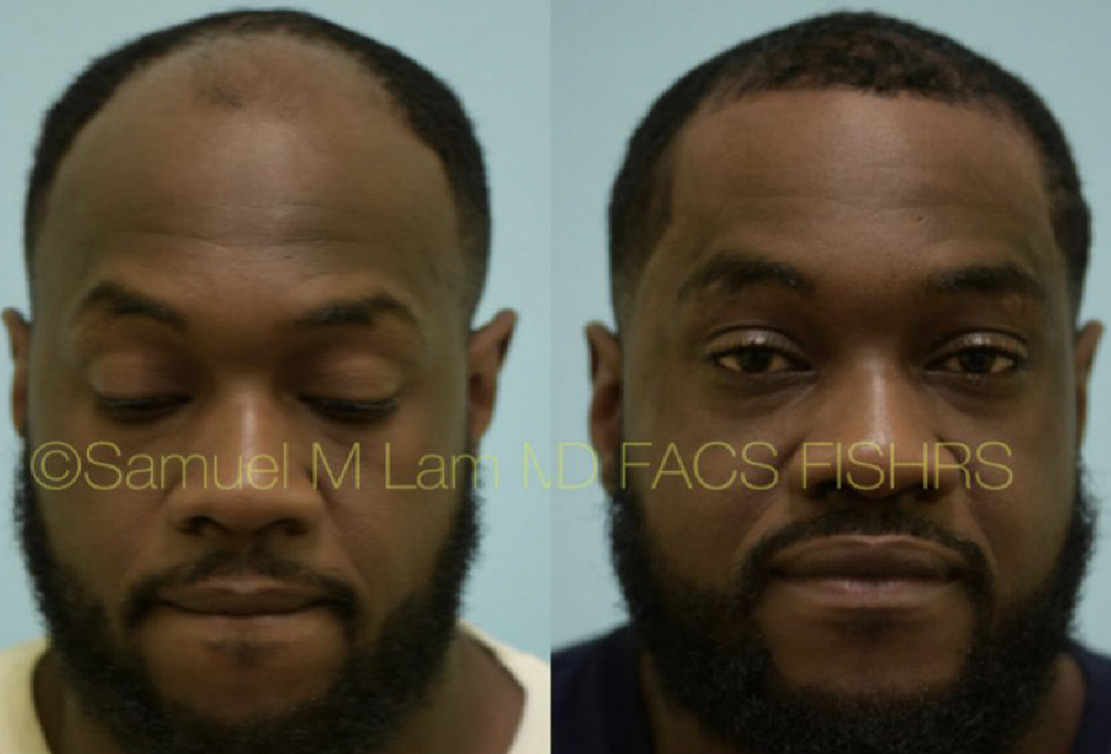
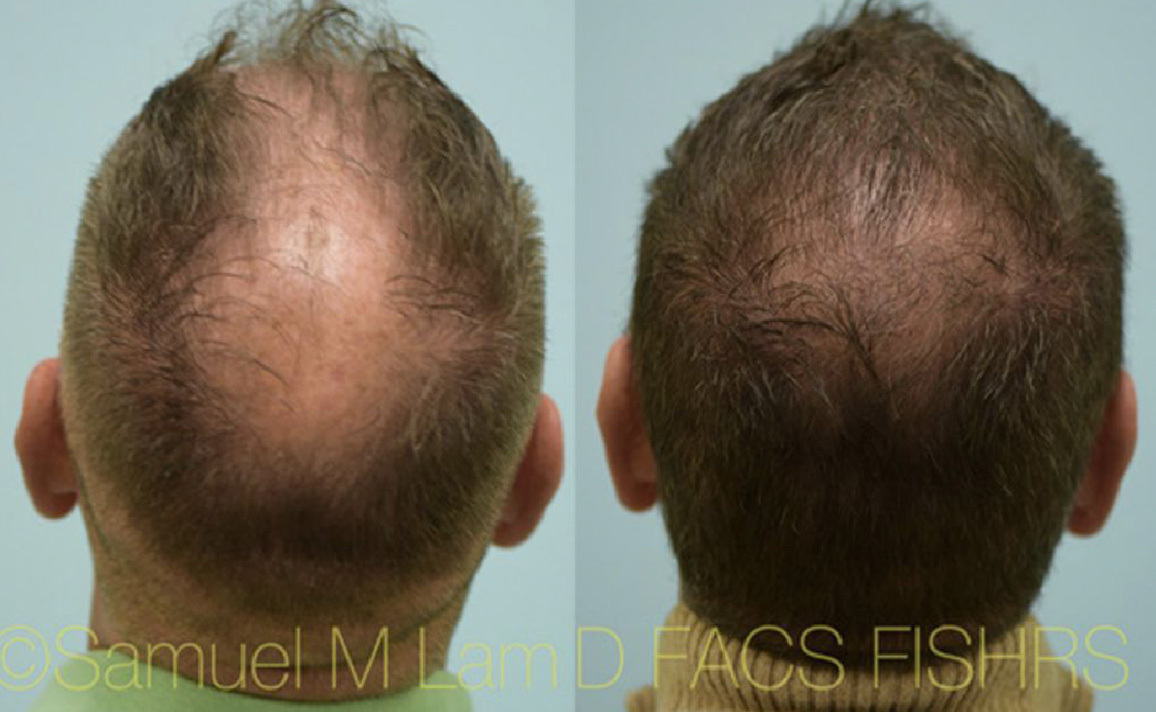
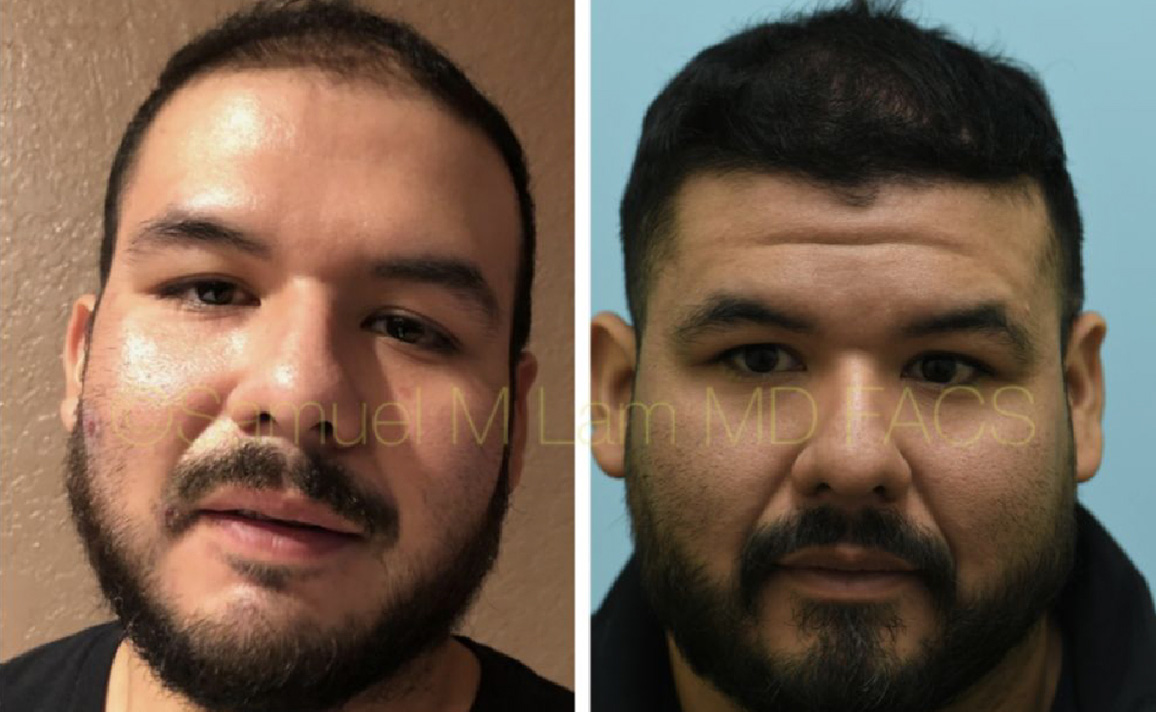
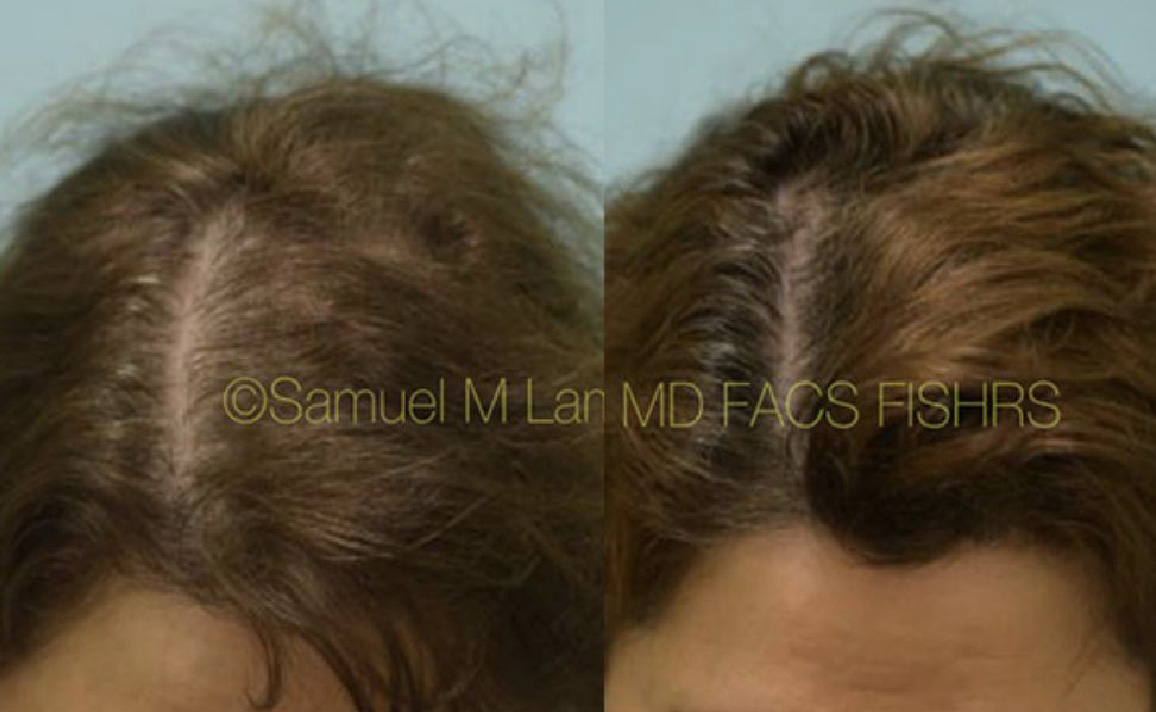
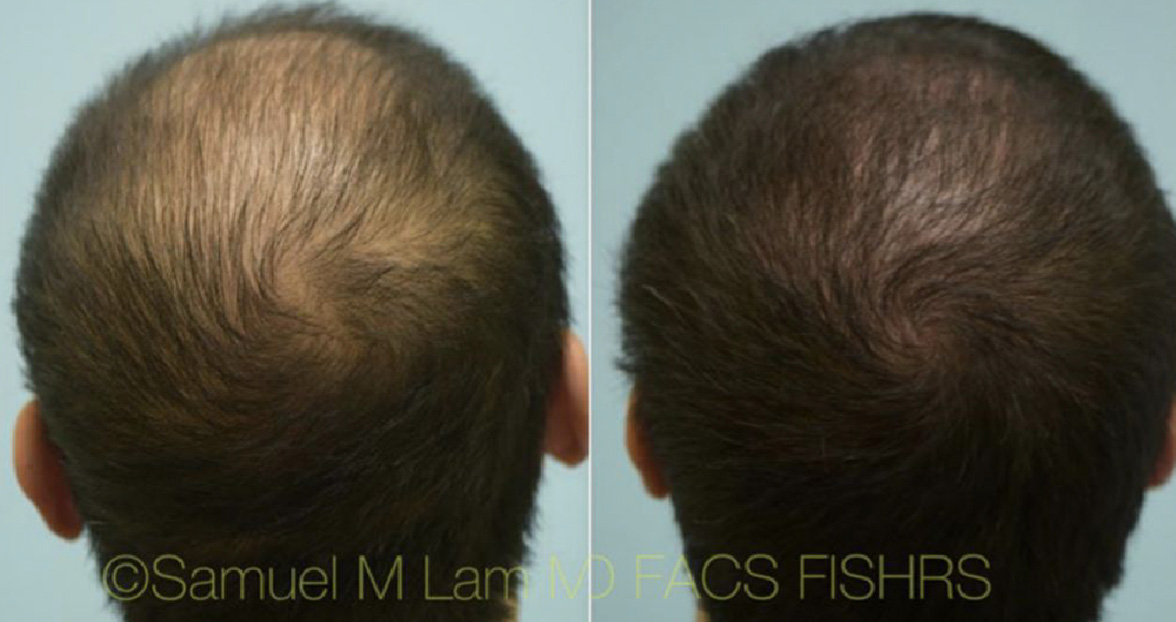
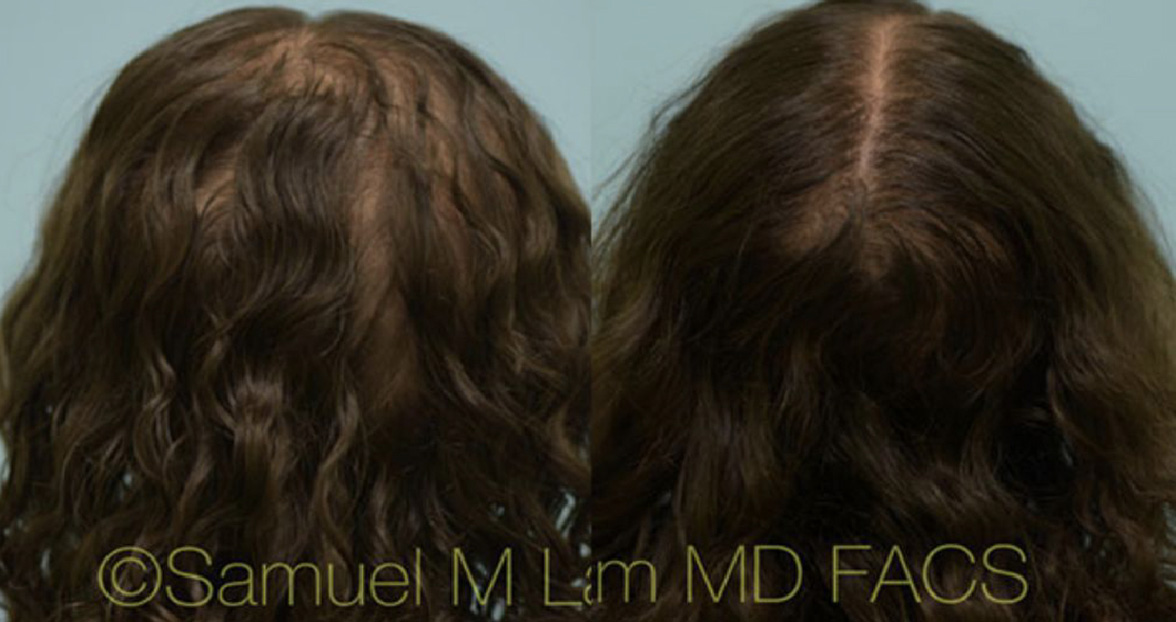
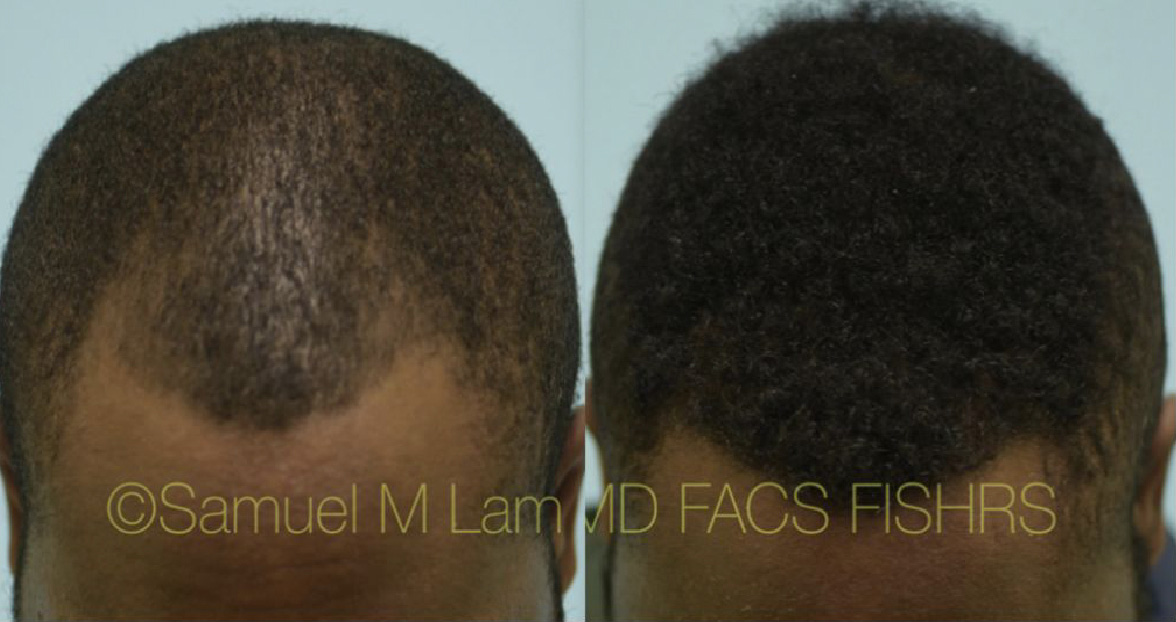
Finasteride & Minoxidil
Hair loss affects half of men over 50 and nearly 20% of women in the United States. Genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, stress, and aging can all cause hair loss, but it can happen to anyone. Gradually thinning hair on the top of the head, a receding hairline, and patchy bald spots are common symptoms of hair loss occurring gradually or suddenly.
Contact Us Today! Read Our Manifesto Visit Our Gallery
ORAL FINASTERIDE
The progression of hair loss is expressed in two ways:
- Shortening of the hair-growth cycle
- Diminishing of the hair-shaft size/diameter
In other words, hair loss is seen as a process of hairs shrinking from healthy terminal hairs that progressively miniaturize to fine, vellus hairs. Since hair is commonly associated with attractiveness and vitality, hair loss can be an unwelcome and traumatizing experience.
Fortunately, there are several FDA-approved medications for hair loss in men and women that slow down hair loss progression as well as promote regrowth and add thickness and density. They can be used separately or combined and delivered orally or topically.
(brand-name Propecia) is a daily medication that helps to slow down and somewhat reverse male-pattern baldness. The mechanism by which finasteride works is through blocking the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) via enzyme 5-alpha-reductase Type 2.
With less DHT present, fewer hairs are susceptible to the hair-loss process; some grow again, and others grow thicker. Finasteride takes several months of usage before visible signs of growth are present. Although the standard oral 1 mg dose is highly effective, Dallas hair transplant surgeon Dr. Sam Lam believes that a genomic evaluation using saliva can help fine-tune your dosing for optimal results. The Hair Genome Test can offer a very precise dosing regimen based on your genetic sensitivity and resistance.
Finasteride is highly effective and works in 99% of men who take it. Some patients have decided that it did not work for them, but this is usually because they either failed to notice the difference (which is why we have standardized photography) or they continued to lose more hair despite the benefits.
Although finasteride can slow down hair loss progression and improve hair growth, younger men with rapid hair loss could still experience hair-loss progression. In addition, some men may not notice a difference with the use of finasteride because their baldness pattern is beyond what it can accomplish. That is, when the area is simply bald with no hairs, the likelihood of finasteride working greatly diminishes.
Oral finasteride has received negative press regarding unwanted sexual side effects. However, Dr. Lam still believes it is overall a very safe and effective therapy, especially to treat male-pattern baldness. He uses various alternative modes of delivery to minimize the risk of side effects in men and women who are sensitive to the oral regimen, such as topical finasteride and injectable dutasteride, the latter of which has no truly reported sexual side effects.
In today’s culture, the use of testosterone pills, creams, injections, and similar modalities has, unfortunately, accelerated hair loss in men who are already sensitive to the effects of DHT. Although testosterone can be safely taken by men who do not have signs of hair loss, those who are must be hyper-aware of this risk. Tracking one’s hair loss history can also be helpful by noting whether it has more rapidly progressed while on testosterone. Unfortunately, there is no direct link between a testosterone numerical value in your blood and what may cause hair loss, since everyone reacts and responds differently to the effects of testosterone. If you are on testosterone, you might truly consider the importance of using finasteride of some kind.
After starting the therapy, the change in hair appearance may be evident as early as 4-6 months and should continue to improve over the ensuing months. Your hair should slow down in shedding, and you could see an improvement in hair count and volume. We will follow up with you to take photos and monitor your progress. Contact our office to learn if you are a good candidate for oral finasteride.
ORAL MINOXIDIL
was traditionally offered as a topical/scalp treatment (marketed as Rogaine) for hair loss. However, over the past few years, oral minoxidil has become a more common treatment, showing effectiveness in slowing down hair loss and improving hair density in both men and women.
Oral minoxidil is given as a single pill once a day, usually starting at 1.25 to 2.5 mg for women and 2.5 to 5 mg for men. It can easily be dosed lower if side effects occur. The effectiveness of oral minoxidil may be higher than the topical version in some individuals, since 30-50% of patients have a reduced level of an enzyme known as sulfotransferase. This scalp enzyme is required to convert minoxidil into its active metabolite minoxidil sulfate. The oral route bypasses the need for scalp conversion of minoxidil. For that reason, oral minoxidil is more effective (for some patients) than topical minoxidil. Furthermore, because topical treatment can affect hairstyling, oral minoxidil offers a much easier and more compliant route of delivery. It can also be compounded with oral finasteride into a single pill. These genetic limitations can be determined via the Hair Genome Test.
After starting the therapy, your hair may show an improvement in hair count and volume as early as 4-6 months, and they should continue to improve over the ensuing months. However, initially, you might notice an increase in hair shedding, which is an indication that the medication is working. We will follow up with you to take photos and monitor your progress. Contact our office to learn if you are a good candidate for oral minoxidil.
TOPICAL FINASTERIDE
offers an alternative to oral finasteride for men having issues with side effects with the oral dose. It can easily be combined with topical minoxidil.
Traditionally, finasteride (Propecia) has been administered orally. However, over the past decade, topical finasteride has become increasingly popular for men in Dallas, since the risk of adverse side effects can be minimized as compared with the oral dose. It can also be safely and easily combined with topical minoxidil, along with other beneficial ingredients like tretinoin, prostaglandin inhibitors, and more.
The Hair Genome Test can precisely determine your sensitivity and dosing of topical finasteride based on your genetic profile. Topical finasteride is typically compounded at 0.25%, but might vary depending on the results of your Hair Genome Test.
For example, you may need a higher percentage (like 0.5%) or even a low dose of dutasteride, depending on your genetic profile. Other ingredients, like the dosing of topical minoxidil percentage, tretinoin, glucocorticoids, etc., would also be determined based on the test.
TOPICAL MINOXIDIL
(brand-name Rogaine) helps with hair growth and slows down hair loss. It is acceptable for both men and women and comes in 2% (women) and 5% (men, but now approved for women, too).
Minoxidil works best when it’s started early, right when the first signs of hair loss appear. However, it can still be helpful for both men and women at more advanced stages. It’s a good option for people who notice that their hair isn’t growing as long or as thick as it used to.
The product must be placed directly on the scalp. Do not shower or otherwise expose your scalp to water for four hours. Hair growth results can typically be observed as early as 3-4 months after starting.
The 5% formulation is sold as either a liquid or foam; both have the same efficacy. However, due to the presence of propylene glycol, the liquid has a 22% chance of an allergic reaction, whereas the foam has about a 2% chance of allergy. In general, the liquid is less expensive than the foam. Initially, it may be worth purchasing both to see which product is easier to apply and style, and in case you are allergic to one. However, compounding solutions have fewer incidences of allergic reaction than the products purchased over the counter.
Dallas hair transplant surgeon Dr. Sam Lam believes that the Hair Genome Test is the most precise way to dose you based on your genetic sensitivity and level of resistance to topical minoxidil. For example, approximately 50% of individuals lack sulfotransferase, an enzyme needed to activate minoxidil in the scalp, thereby requiring higher doses for efficacy. Oral minoxidil can also be a suitable alternative for someone looking for an easier compliance regimen.
FAQs About Oral Finasteride
-
Do I need minoxidil or other medical therapies if I am on finasteride?Finasteride offers the strongest benefit for the patient, but all therapies are very helpful when used in combination. Minoxidil works synergistically (or additively) with finasteride.
Someone who has been on finasteride for a long time and then adds minoxidil should see an uptick in improvement. Conversely, a patient who has been on finasteride and minoxidil and stops one or the other product will notice a similar worsening.
Most patients can use as many therapies (minoxidil, laser, and PRP/Hair Stem) as they want, can afford, and can tolerate because all of these methods are additive in their benefits. I will speak with you about the pros and cons of all the medications to help you decide which combination may be ideal for you. -
What are the side effects?The most common side effect of finasteride is a reduction in libido that could, in some patients, lead to erectile dysfunction. In rarer cases, there can be breast tenderness or a change in mood, especially if someone has already been on antidepressants.
The initial studies have shown an incidence of less than 1% compared with placebo for sexual side effects. However, some uncontrolled post-marketing surveys have raised the alarm of permanent sexual side effects in a small group of men.
Although there have been scattered reports, there have been no large-scale clinical reports about this trend. Dr. Lam finds that this medication is not only highly effective but also very safe.
There has also been a documented incident of what is called a nocebo effect, that is, simply counseling someone about the potential for a side effect can lead to the occurrence of a perceived side effect. Of note, men on finasteride cannot donate blood. -
If I experience side effects, what can I do?Initial Merck studies found that 57% of men who continued medications for a month or more had complete resolution of their side effects. Accordingly, it may be worth continuing the medication for a minimum of one month before concluding whether you should keep going.
Another option, if side effects do arise, is to consider taking one pill every other day rather than daily. In Dr. Lam’s experience, doing so has taken care of most issues. The effectiveness of finasteride may be somewhat reduced, but it is still worth taking it at this reduced dosage. -
What if I stop taking medication?Unfortunately, all of the hair that is preserved during the time you are on finasteride will be lost over several months when the medication is stopped. To clarify, if you have been on the medication for 5 years and then stop, the amount of hair that was preserved during that time will be lost (not more hair than you would have lost).
This can be very discouraging to hear, but with such an effective medication available, I like to help your psychology by saying: “Keep taking finasteride for as long as you care that you have hair or until a better medication comes around.”
Of note, there are so many technological breakthroughs that are on their way like prostaglandin modulators (both topical and oral), DNA 3D printing of follicles, etc. However, if you don’t start taking finasteride and wait until these medications arrive on the market, you may have irreversibly lost so much hair that finasteride or another medication will be less effective. Accordingly, you should start your medication as soon as you can and be as compliant as possible. -
What does dutasteride (Avodart) do differently than finasteride (Propecia)?Dutasteride (marketed as Avodart) is a dual alpha-reductase inhibitor blocking both alpha-reductase type 1 and alpha-reductase type 2. Finasteride (Propecia) only blocks type 2. Accordingly, finasteride only blocks about 65% of circulating DHT; whereas dutasteride can block up to 99% of circulating DHT.
Based on the Hair Genome Test, you may be a better candidate for dutasteride, which the test will reveal. Oftentimes, the results of the test will recommend a dose that is not standard but instead tailored to your genetic profile. -
Does finasteride work for women, too?Earlier studies found no benefit in postmenopausal women. More recent studies have shown that finasteride may help postmenopausal women who experience hair loss. Caution should be exercised in women of childbearing age because it can lead to birth defects in children for women who take finasteride during their pregnancy.
The Hair Genome Test will give precise information as to your genetic sensitivity and dose should you desire to incorporate it into your treatment plan with the risks and limitations stated above taken into consideration. Today, Dr. Lam mainly uses all-natural products like Folliflo, Hair Stem, and his invention using Botox to help with hair loss.


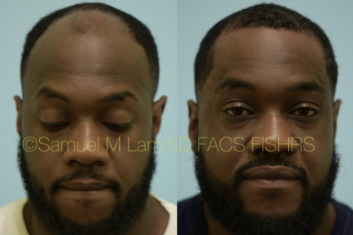
FAQS ABOUT ORAL MINOXIDIL
-
Do I need prescription?Yes, any oral medication requires a prescription. Once you visit our office, we will submit a prescription to the pharmacy of your choice.
-
How should I decide between topical and oral minoxidil?This decision should be made together with Dr. Lam during your consultation. Topical minoxidil has a lower risk of side effects, but a higher chance of a topical allergy like redness and itchiness on the scalp.
Some formulations of topical minoxidil may also leave the scalp greasy or weighed down. Topical formulations can be combined with topical finasteride as a single product. The oral route has the benefit of easier compliance, but also has a slightly higher incidence of side effects. -
If I take minoxidil, do I need to take finasteride?For women of childbearing age, finasteride is not a safe option since it can cause birth deformities. However, in post-menopausal women, finasteride may be combined with minoxidil.
Men will usually benefit from taking both medications; for women, the responsiveness to the medication varies due to the myriad of reasons they experience hair loss.
In general, the two medications are synergistic in that they work better together rather than alone. If you take the Hair Genome Test, you may find that you are more resistant to minoxidil or finasteride, which will help us tailor your treatment accordingly. -
Are there any conditions that would preclude me from taking oral minoxidil?In general, if you have significant cardiac (heart) issues, it may be safer to avoid oral minoxidil and use the topical version. As mentioned, if you are experiencing any adverse symptoms that are not resolved by reducing the oral dose, then you may need to convert to using a topical formulation.
-
What are the side effects?Oral minoxidil has a slightly higher side effect risk compared with topical minoxidil, including lower blood pressure, swelling in the legs, dizziness/headaches, allergic reaction, and heart palpitations (feeling the heart beating fast). The chance of each of these effects is about 1%. There is also a 15% chance of unwanted hair growth elsewhere other than the scalp for women.
-
If I experience side effects, what can I do?In general, the incidence of facial hair growth from an oral dose is slightly higher than from topical minoxidil (15% vs. 5%, respectively). In the few women who get facial hair growth, they actually notice the most remarkable amount on their scalp. Some elect to continue with the therapy despite the unwanted hair growth elsewhere. However, if you experience palpitations or swelling, they should go away after stopping the medication.
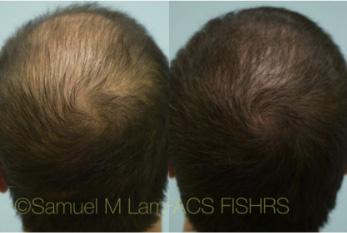
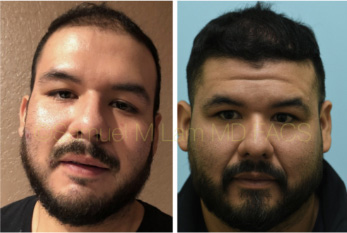
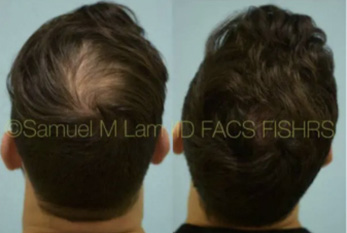
FAQS ABOUT TOPICAL FINASTERIDE
-
-
Is topical finasteride as effective as oral finasteride?Usually, yes, but not necessarily for everyone. In the past, Dr. Lam would experiment to see which one you would respond better to, but now, with the Hair Genome Test, he can titrate close to exact equivalents between the two routes of delivery. That way, you can easily switch between the two with similar — if not the same — results.
-
What if I skip a few days of usage?You can skip a few days and usually not have any issues or lose ground with your therapy. However, like oral finasteride (or any route of minoxidil), you should not skip a month or two of the product, or you will lose what you’ve gained since the beginning of treatment. Consistency is key, but missing a few days to a week is okay, even though it is not preferred.
-
If I am on the oral version, can I switch to the topical one?Yes, and vice versa. You will find which one is better for you based on compliance, side effects, and other patient-specific factors. Dr. Lam and his team will work with you to determine the best route of delivery.
-
Are there any side effects?Although topical finasteride has shown a lower incidence of side effects in comparison to oral finasteride, there are still chances of side effects occurring. The most common side effect of finasteride is a reduction in libido that could, in some patients, lead to erectile dysfunction. However, it is important to know that due to the possibility of accidental ingestion, topical finasteride is not recommended for men who are in close contact with a pregnant woman.
-
If I experience side effects, what can I do?In some cases, a reduced dosage can still show effectiveness but eliminate a side effect. You can either reduce the daily dosage or keep the same dose by applying it every other day.
-
Can the medication be shipped to me?Yes, we will submit the prescription to a compounding pharmacy, which will then ship the medication directly to you.
-
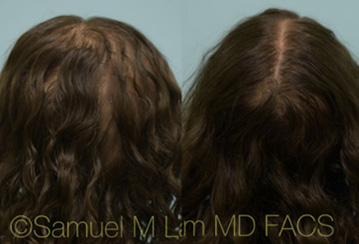
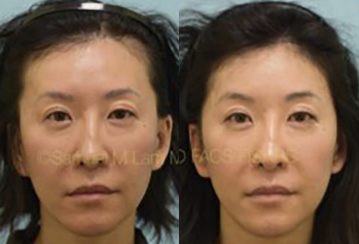
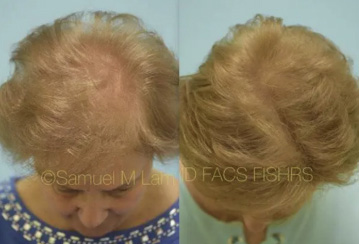
FAQS ABOUT TOPICAL MINOXIDIL
-
How many times a day should you apply minoxidil?Initially, topical minoxidil was recommended to be applied twice daily but most individuals have a hard time complying with using it twice a day. That is why Dr. Lam recommends doubling the dose and applying it just once a day.
Some reports have shown the benefit to be very similar between a once and a twice-a-day regimen. If you can easily apply the product twice a day, then do so. -
Is it true that minoxidil works only in the crown but not in the front of the head?This is false. The initial FDA trials only evaluated the crown, so the package insert on over the counter minoxidil has to reflect the parameters of those clinical trials. Nevertheless, subsequent to those trials, studies have shown that minoxidil works very well in the front and back of the scalp.
-
What will happen if I stop using minoxidil?In short, you will have lost what you gained or retained during the time you were on it. Unfortunately, all of the hair that is preserved during the time you are on minoxidil will be lost over 3 to 6 months after stopping the application.Stopping the product suddenly may cause the onset of hair shedding. Dr. Lam recommends phasing out minoxidil and using his Folliflo serum to mitigate shedding.
-
Do I need other therapies beside minoxidil?In short, yes, if possible. Minoxidil works synergistically (or additively) with finasteride (which, to be clear, is only for men). Someone who has been on finasteride for a long time and then adds minoxidil should see an uptick in improvement.
Conversely, someone who has been on both finasteride and minoxidil and who stops one or the other product will notice a similar worsening. As many therapies (finasteride, minoxidil, laser, supplements, and hair stem therapy) that you can afford, tolerate, and desire, you should consider because all of them are additive in their benefits. Dr. Lam will consult with you on the pros and cons of all the treatments to help you decide which combination may be ideal for you. -
Do I really need minoxidil if I’m planning to have hair transplant surgery?Possibly. The first reason to have minoxidil, even though you are planning to have hair transplant surgery, is stated above: to reduce the risk of shedding after a procedure. The second reason is also stated in this section, which is to help with further hair loss that may occur as one continues to age.
Dr. Lam will discuss the pros and cons of short and long-term use of minoxidil as it relates to your situation during your consultation. However, today, he recommends Folliflo as the easiest and most effective way to manage shedding around the time of a transplant procedure. -
Are there any side effects?In some cases, topical minoxidil can cause scalp irritation, palpitations, headaches, and/or facial hair growth. Decreasing dosing, changing from the liquid to the foam form of minoxidil, or stopping the product should eliminate these side effects. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not use minoxidil, and women who are trying to get pregnant should stop using minoxidil.